Introduction
Decomposition is a Mixed Process Ranging from Autolysis of Individual cells by Internal chemical breakdown to tissue autolysis from liberated enzymes, and External process introduced by Bacteria and Fungi from the intestine and outer Environment. Animal Predators, from Maggots to Mammals, can be included in the range of destruction.1, 2 Decomposition may differ from body to body, from environment to Environment, and even from one part of the same corpse to another. sometimes one portion of a Corpse may show Leathery, mummified preservation whilst the rest is in a state of Liquefying Putrefaction.3 The above Physico Chemical Changes are Naturally Occurring in the Dead Bodies. However, they are mostly seen in those bodies which are Abandoned and were Unrecoverable bodies. But there are numerous instances wherein the Bodies get Decomposed due Humane Factors like Delayed Reporting of Death, Delayed Shifting of the Dead, Storage Factors, Social, Cultural and Circumstances Under which they were Recovered. In Majority of Forensic Autopsy Less Importance is Given to understand the Factors that lead to Changes in Bodies after Death and more importance is Given to understand the Cause and Manner of Death. Hence This Study is one Such Maiden Attempt to understand the Human Factors responsible for Decomposition and understanding its effects in finding the Cause of Death in such Decomposed bodies.
Materials & Methods
The Study was carried on all Decomposed Bodies Referred during the period 2010 to 2021, at Jamaica and Bangalore. The Decomposed bodies were Registered in a separate Bok and all the Particulars like Age, Sex, Place of Death [Death Scene], Causes of Death after Autopsy, Identified and Unidentified Bodies and Factors responsible for the state of Decomposed Body was closely Studied. The Death Scene Photos, Family members & Friends Inputs beside Visit to the Death scene was made. All the Data Thus collected were entered in a Standard Table for Each Parameters and the Result thus obtained were carefully analyzed. The Early Decomposition changes was considered Mild and The Changes like Blisters and Sloughining of Skin, Swelling and discoloration, Marbling were Considered as Moderate State and All other Signs of Decomposition like Liquefaction with cavity rupture and soft tissue detachment from Bones were considered as delayed Signs [Advanced Decomposition]. Decomposed bodies without soft tissues were considered as skeletonised bodies as a late sign of decomposition.
Results
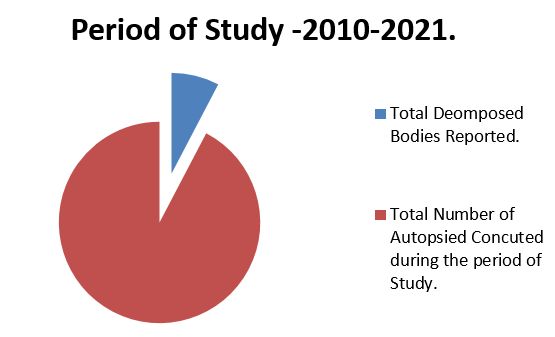
The Study was carried at Two places Jamaica & Bangalore during the Period 2010 to 2021. A total of 7456 cases [Figure 1] were Autopsied During this period and Decomposed Bodies constituted 620 cases. [Table 1]. Males Contributed to 82.6% [n-512] of cases and Females contributed to 17.4% [n- 108] cases
Table 1
Total number of cases and their sex distribution during the period of study [2010-2021].
Table 2
Indicates the total identified and unidentified decomposed bodies and country reported during the period of study.
|
Unidentified /Unclaimed Bodies |
212 |
|
Identified Bodies |
408 |
|
Jamaica[21010-2012] |
531 |
|
Bangalore,India[2013-2021] |
89 |
Majority of the Decomposed bodies [n-408/ 65.8%] were Identified Bodies and had Family Members to Claim those bodies. In 34.2% [n-212] of Decomposed Bodies were Unidentified and were Unclaimed Bodies. Majority of the cases [n-494/85.6%] cases were studied in Jamaica [3years] and only 14.4% [n-89] were reported in India [Bangalore] for 09years.
Table 3
Age group involved
|
Age Group |
Total |
|
0-10 |
00 |
|
11-20 |
00 |
|
21-30 |
21 |
|
31-40 |
35 |
|
41-50 |
68 |
|
51-60 |
124 |
|
61-70 |
306 |
|
71-80 |
57 |
|
81-90 |
09 |
Table 3 Indicates the Age group Distribution of Cases. Maximum Decomposition cases belonged to the Sixth Decade followed by Fifth Decade Individuals. None were reported below the Second Decade groups. Least reported from the Eighth Decade Group. Overall Majority of the cases were reported from the individuals whose age ranged from 40-80years.
Table 4
Death scene
|
Place of Residence |
Around the Place of Residence |
Unclaimed Bodies Morgue |
Other than Residence & Surroundings |
|
390 |
108 |
124 |
68 |
Indicates the Death Scenewhere the bodies were Found and Recovered. In 62.9% [n-390] cases the Bodies were Recovered from the Place of Residence. In 17.4% [n-108] were those recovered from around the place of residence like garden, walkways, Roadside, riverside, farm etc. In 20% [n-124] of cases the Bodies were found Decomposed in the Morgue and all were unclaimed Bodies which were preserved pending Identification for more than Four Weeks. In 11% [n-68] of cases the bodies were Discovered away from the place of Residence or Immediate surroundings. They were located in Strange places and Uninhabitated Places.
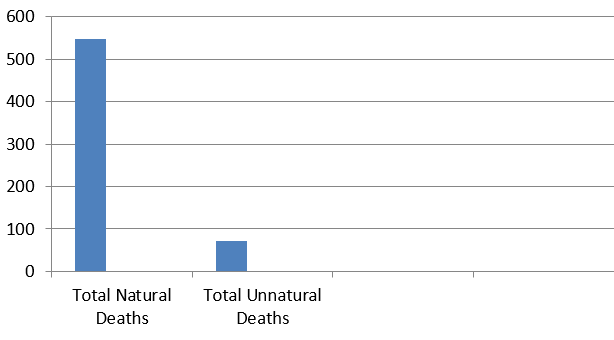
The above Tabel Indicates that MAjority of Decomposed Bodies Referred had died due to Natural Causes, this contributed to 88.4% [n-548] of Cases and Unnatural Deaths contributed to only 11.6% [n-72] of the cases.
Table 6
Causes of natural deaths
Indicates the Different Type of Natural Deaths Examined in the Decomposed Bodies of which UNDETERMINED [n-306] contributed to 55.8% of cases, this was followed closely by Individuals dying due to Ischemic Heart Disease/COPD contributing to 13.5% of cases [n-74]. Cerebravaascular Haemorrhage were the least reported, contributing to 1.5% [n-08] of the cases. Congestive Cardiac Failure and Cancer Contributed to 16 and 20 Cases Respectively. Generalised Sepsis [n-46] and Malnutrition [n-32] cases were also reported during the period of study.4
Table 7
Causes of unnatural deaths
|
Sl No |
Un Natural Causes of Death |
Total-72 |
|
1 |
Gun Shots |
28 |
|
2 |
Road Traffic Accidents |
24 |
|
3 |
Hanging/Strangulation |
02 |
|
4 |
Bludgeon /Crush Injury to Head |
04 |
|
5 |
Chop/Stab Injury |
08 |
|
6 |
Drowning |
06 |
Indicates the Unnatural Causes of Death in the Decomposed bodies. Only 72 cases [11.6%] of Decomposed Bodies Died as a result of Unnatural causes of which Gunshots Deaths contributed to 38.9% [n-28] followed closely by Road Traffic Collision Deaths in 33.3 [n-24] deaths. The other Unnatural causes that were reported were Drowning [n-06], Stab/Chop injuries [n-08], Hanging/Strangulation [n-02] and Crushing Head Injuries [n-04].
Table 8
State of decomposed bodies
|
State of Decomposition |
Total-620 |
|
Early |
86 |
|
Moderate |
134 |
|
Advanced/Late |
314 |
|
Skeletonisation |
48 |
|
Adipocere Formation |
24 |
|
Mummification |
14 |
Indicates the State of Decompositon at the Time of Autopsy Examination. MAjority of cases [n-314/ 50.6%] the bodies were in a, avanced state of DEcompositon. In 21.6% [n-134] of cases the Bodies were Moderatly DEcomposed. Early Signs of decomposition were reported in 14.3% [n-86] of cases.in 7.7% [n-48] of cases the Bodies were skeletonised without Softtissues attached. wheras Adipocere and Mummiication were reported in 24 and 14 cases respectively.
Table 9
Factorsresponsible for decomposition
Indicates the Facros that were responsible for the Decomposition. Majority of the Decomposed bodies [n-279/ 45%] the individuals lead a Lonely life followed closely from those bodies which were Unclaimed or Unidentified [n-212/34.2%]. In 10.5% [n-65] of cases the bodies were recovered from an Unhabitated or Inaccessible regions. In 4.2% [n-26] of cases the Decomposition was due to Delayed Information or Late reporting of the body from the Death Scene. The Technical issues Surrounding the Morgue/Presrvation of the Dead contributed to 3.9% [n-21] of Decomposition. Delay in Postmortem or Body Awaiting postmortem factors contributed to 1.5% [n-9] of Decomposition and Prolonged Storage of bodies contributed to 1.3% [n-8] of Decomposed bodies.
Discussion
Decomposed bodies referred to Autopsy is Not Uncommon during the Course of Forensic Examination. This Circumstances always pose a challenge to the Autopsy Surgeon, both in terms of finding the Causes of Death and also Understanding the Reason for the Such State of Decomposition. The present Study is One Such wherein the Factors that were Responsible for Decomposition were closely analyzed besides understanding the causes of Death. In this Study a Total of 620 cases [Table 1] of Decomposed bodies were Examined during the period 2010-2021, of the 620 cases examined Males Contributed to the 82.6% of the Cases [N-512] and Females contributed to only 17.4% [N-108] cases, similar were the observations made by Singh et al.(2016), 5 Cyriac job(2009)6 & Ambade et al.(2011).7 In One such Study of Decomposed Bodies by R.Ban & Dutta (2018),8 only 78 cases were reported during their Three and Half Year of Study. hence, this study draws an edge as to the high number of cases reported which helps to draw more scientific conclusions. Majority of the cases [Table 1] in the early years of Study were Reported from Jamaica [2010-2012] and Few cases were reported from Bangalore, India [2013-2021]. Hence, the Regional and Social and Cultural Factors play an Important Role in the Decomposition of Bodies. Similar were the observations made by R.Ban & Dutta8 and Ambade et al.(2011),7 wherein Regional factors played important role in the number of cases reported.
The Major Social and Cultural difference in Jamaica & Noted were, the Lonely Life of the Individuals, degenerated Family life as a result of Divorce or Migration to USA & Canada for Better Life Leaving Behind Parents, thereby rendering the Senile Individuals without Caretakers. Hence Any Medical Emergency gone Unreported, unlike India wherein the Elderly were always closely stayed with their Children mainly Male Siblings. Abandoning Parents were Considered as a Major Moral Crime that lead to social outcast and their Family members were Easily identified in the society. Majority [n-390]of the cases were reported from the place of Residence, this clearly confirms the Lonely life with absence of Care takers in Senile individuals as the major factors responsible for the Decomposition, it was the smell emanating from the place of residence and alert neighbors which lead to the Decomposed Bodies. similar were the reasons for the bodies recovered from the surroundings [n-108]of the place of residence. As discussed above the Unclaimed bodies [n-124] that were unsuccessfully waiting for Family members, this prolonged delay both in information of death, Transportation and technical issues surrounding the preservation of the dead all played an important role in Encouraging the Decomposition process. Few cases [n-68] were reported from those region that were in remote areas or inaccessible regions, the major reasons were delayed information or shifting of the dead, majority of those recovered were Nearly skeletonisation and mutilated by Canine Animals. The Major Group of Individuals [n-548] died as a Result of Natural causes [Figure 2]and very few were due to Unnatural Causes [n-72]. The Majority of Natural Causes of Death go Undetermined as a result of Decomposition of Tissues and Organs, this were reported in 55.8% of cases [n-306] and in only 44.2% of Natural death cases Cause of Death were Identified of which COPD [Chronic obstructive Pulmonary Disease] and IHD[Ischemic Heart Disease that were noted in 74 Cases. The Least Reported were in Rheumatic Heart Disease, & Cerebrovascular Accidents, which reported in only 08 cases. Hence, Decomposition directly Interfered in the Cause of Death Determination due to destruction of the Tissues and Only in Early decomposition [Figure 3]and few Moderate Decomposition cases[Figure 4] the Natural Causes of Death were Determined. This results are in contrast to those made by R. ban & Dutta (2018),8 wherein he was able to Ascertain Cause of Death 70.51% of his cases, similarly Cyriac Job(2009)6 was able to conclude Cause of Death in 71.63% of his cases.
The Common Unnatural Causes [Table 7] reported were due to Gunshots and Road Traffic Collision which were seen in 28 and 24 cases respectively. The least reported Unnatural Causes of death wherein Decomposition were noted were Asphyxial deaths like Strangulation/Hanging and Drowning which reported in 02 and 06 cases respectively. This observations are in contrast to those made by Singh et al.(2015) wherein Asphyxial Death were major causes of Death, this is because of the regional influence wherein in Jamaica due to the Gun Culture more Gunshots were reported. In all this Unnatural cases as discussed above they were reported in Inaccessible region and remote areas to conceal crime and destroy the evidence including the identity. In this Study Majority, i.e 50.6%, of the bodies [n-314] recovered were in a Advanced State of Decomposition, this clearly reflects the Lack of reporting of Death or delayed Information and recovery. The observations are closer to those made by Singh et al.(2015)5 and R. ban & Dutta.8 Skeletonisation9 [Figure 5]were noted in 7.7% [n- 48] cases, this were seen in majority of Unnatural deaths and from those bodies that were recovered from Remote Inaccessible regions, the possibility of Kidnapping, Murder and destruction of evidence and Identity.10 as motive for this Decomposition cannot be ruled out. Mummification11 [Figure 6]were reported in 14 cases, and Adipocere 12 Formation were seen in 24 cases, this clearly reflects the place and region of recovery of the bodies played important role though the bodies were recovered after few weeks to months. Hence, more the Delay in information, Recovery and Transportation of the dead More the Decomposition process which interfered in the Identity, Cause of Death besides destroying Evidence ,all this posed a Greater Challenge to the Forensic Pathologist and the Investigating officer. Hence, the Study confirms that Single Family Member or Lonely Life Individuals death goes unreported due to lack of Care takers and lack of Death information and this delay lead to Decomposition of the body during the time of recovery.
The Unclaimed Bodies pending Identity and Arrival of Family members also contribute to delayed information and reporting of the death during the time of recovery, beside this the further delay cause for identity process and claims during the Improper Storage of those bodies lead to Decomposition that were seen in 212 cases. Delay i Postmortem also lea to decomposition, this is due to failure to store the body awaiting police Request for Autopsy in already delayed recovery of the identified bodies.
Conclusion
Lonely and Elderly Individuals need to be closely monitored and cared. Local Health Authorities need to closely monitor, their Responsibility should be Laid down on their Sibling a suitable legislation should be introduced. Individuals Living a Lonely Life and Dyeing in their place of Residence were the Major Group of Individuals wherein Decomposition were Reported. Majority of the Deaths were due to Natural Causes with fewr Unnatural Deaths. A systematic mechanism should be developed for Timely Reporting of Death and early shifting of Dead to a Well equipped Morgue. Decomposition interferes in the Identifying causes of Death in Majority of the Natural Deaths thereby Interfering in understand the Disease Process and Manner of Death. Hence, Timely Confirming the Death and Shifting the Dead and Proper Storage is essential in all Forensic Autopsy cases.